A barcode is made up of a series of lines and spaces that represent digital information.
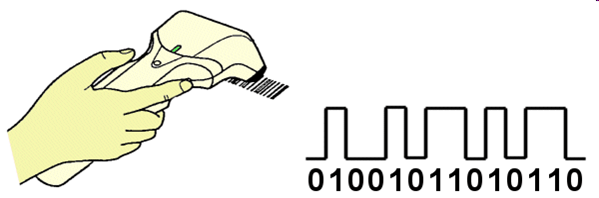
When a barcode is read by a scanner, the thickness of the lines and spaces is measured, on the basis of which a binary code is created.
What is a barcode for and what are its benefits:
1. Accuracy.
When using a barcode, the chance of making a mistake is 1 character in 1 million to 1 billion.
When entering data manually, the error rate is typically 1 character in 300 characters.
2. Quickness.
It takes less than 1 second to enter 12 characters with a barcode scanner. With manual entry, this takes about 6 seconds.
3. Ease.
Printing and reading barcodes is a very simple process that saves time and guarantees the accuracy of reading / data entry.
Barcode types
- Linear (1D)
There are many standard barcode types used by various applications. Everyone chooses one or the other 1D code, depending on the type of data they would like to have in the code.

Most popular barcodes
Numeric barcodes:
EAN13: European barcode standard, which is designed to encode the product and manufacturer identifier
EAN8: compressed version of the EAN code for use on small products
UPC-A: universal product code that can be seen on almost all retail products in the US and Canada.
Alpha Numeric Barcodes:
Code 129: makes it possible to encode not only numbers, but also letters of the Latin alphabet, as well as special characters.
Code 39: is general purpose code.
Code 93: is compact code similar to code 39.
- Two-dimensional (2D)
– 2D codes can be read in any direction
– Significantly larger data capacity than linear barcodes (up to 2000 characters)

The most popular 2D codes:
DataMatrix can store large amounts of data, especially suitable for creating very small codes
PDF417 rectangular barcode, great for encoding large amounts of data
QR code is the number one barcode for marketing applications (URL, etc.)
The GS1 DataBar is able to encode the GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) on small-sized consumer products that are difficult to apply standard labeling (EAN-13 character), such as fresh (by weight) products, jewelry, or products like ” do it yourself”. The GS1 DataBar barcode symbol can encode additional information such as weight, expiration date, lot number, etc.

